“From DNS resolution to security, this guide covers it all. Elevate your understanding of DNS and optimize its performance for a seamless online experience.”
Introduction to DNS
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental technology that powers the internet. It serves as the internet’s phone book, translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing us to access websites and services. In this guide, we’ll delve into the workings of DNS, its importance, and essential terminology.
How DNS Resolution Works
DNS resolution is the process of converting a domain name into an IP address. When you enter a URL into your browser, your device queries DNS servers to find the IP address associated with that domain. This process involves several steps, from local DNS caches to authoritative DNS servers.
Understanding DNS Hierarchy
DNS operates in a hierarchical structure. At the top are Top-Level Domains (TLDs), like .com or .org. Below them are Second-Level Domains (SLDs), such as google.com, and further down, we have subdomains like www.google.com. This hierarchy plays a crucial role in organizing and routing internet traffic.
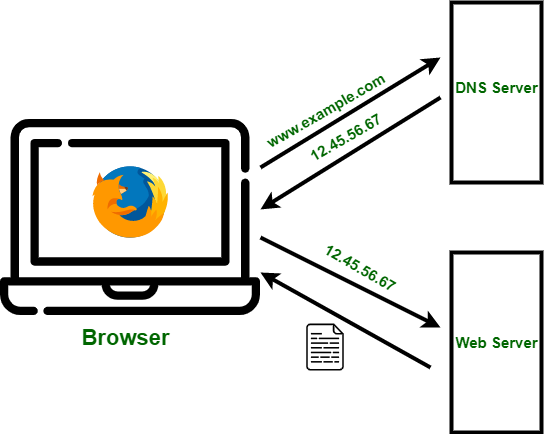
Working of DNS
- Domain Name Request: When you enter a domain name (e.g., www.example.com) in your web browser, your device needs to find the corresponding IP address to reach the website.
- DNS Query: Your device sends a DNS query to a DNS resolver (typically provided by your ISP or a public DNS service like Google DNS). This resolver is responsible for finding the IP address associated with the domain.
- Caching: DNS resolvers often have cached information. If the IP address for the domain is found in the cache, the resolver can quickly provide it without further processing. This caching improves response times.
- Recursive Search: If the IP address is not in the cache, the DNS resolver initiates a recursive search. It starts by querying the root DNS servers, which direct the resolver to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) server.
- Iterative Queries: The TLD server directs the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the specific domain (e.g., example.com). The resolver sends iterative queries until it reaches the authoritative server.
- Response: The authoritative DNS server provides the IP address for the requested domain back to the resolver.
- Return to User: The DNS resolver caches the IP address and sends it to your device. Your device can now connect to the webserver associated with the domain.
DNS is a distributed and hierarchical system, ensuring efficient and accurate domain name resolution across the internet.

DNS Record Types
DNS uses various record types to store information about domains. Here are some common ones:
- A Records: Maps a domain to an IPv4 address.
- CNAME Records: Redirects one domain to another.
- MX Records: Specifies mail servers for a domain.
- PTR Records: Resolves an IP address back to a domain name.
- NS Records: Identifies authoritative name servers for a domain.
DNS Cache and Its Role
DNS caching involves storing DNS information locally to speed up future queries. This improves efficiency and reduces the load on DNS servers. Caches can exist at various levels, from your device’s cache to your ISP’s cache.
Common DNS Issues and Troubleshooting
DNS problems can disrupt your internet experience. Learn how to identify issues like DNS resolution failures and slow lookups. Tools like nslookup and dig can help diagnose and resolve these problems.
Securing Your DNS
DNS security is critical to safeguarding your online presence. DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) add a layer of security to DNS by ensuring data integrity and authenticity. Implementing best practices like regular updates and monitoring can further protect your DNS infrastructure.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the inner workings of DNS, from its hierarchical structure to the role of various DNS record types. Understanding DNS is crucial for anyone navigating the internet, and by following best practices, you can optimize its performance and security. As technology evolves, so does DNS, making it an ever-important part of our connected world.





